RETURNING TO THE LAND OF OPPORTUNITIES, AND FIERCE COMPETITION: HOW TO JUMPSTART A CAREER IN CHINA
Between a perceived glass ceiling overseas and intense job competition in China, many Chinese who have gone to university or graduate schools abroad are discovering that desirable employment is not that easy to come by.
With a surprisingly robust GDP growth of 6.9% in Q1 2017, the largest increase in the past year and half, many global investors are bullish on the Chinese economy as it shifts away from export-led manufacturing. Powered by government investment in crucial technologies and industries, such as clean energy, advanced materials and the like, China is on the threshold of a game-changing transition to become the world’s leading economy. Coinciding with an overseas backlash against the globalization that has underpinned China’s past thirty years of economic development, this vision of China’s dynamism is attracting returnees and foreigners alike to build a career in China.
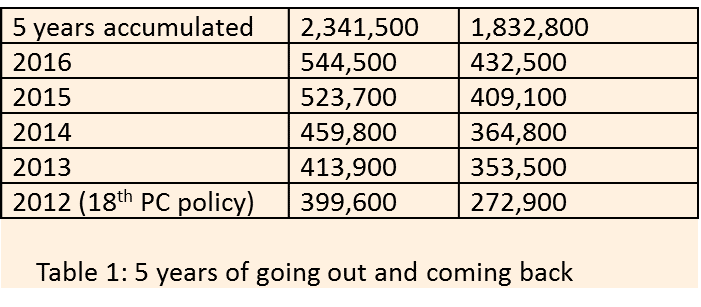
According China’s Ministry of Education, more than 4 million Chinese nationals studied abroad from 1978 to 2016. 2.2 million of them have since returned to China, with the pace of return accelerating in the past few years. The Chinese government since 2012 has increasingly promoted favorable policies for bringing “overseas talent” back to China. Many Chinese students never really adjusted to the cultural or linguistic environments in their host country. China’s continuing high economic growth has created a sense of dynamic professional opportunities. It is no wonder that more and more Chinese professionals are opting to return to their native land.
But, according to a report on overseas returnees published at the end of 2016, more than 60 percent of those who have found jobs work in lower than desired positions with salaries that fall short of their expectations. The large number of returnees have similar backgrounds and are similarly competitive. They are all seeking jobs in first-tier cities, as are the millions of domestic college graduates, and thousands of people apply for every advertised position. Unlike even ten years ago, it is difficult to distinguish oneself from the competition. Returnees also suffer from having to adapt to a business and work environment that is very different from when they left. Domestic graduates remained embedded in local networks and retain familiarity with the Chinese environment.
A CEO survey conducted by PwC (January 2017) found that 77% of CEOs interviewed worry that skills shortages could impair their company’s growth. And they say it’s the soft skills they value most that are hardest to find. Creative, innovative leaders with emotional intelligence are in very short supply. If anything, indeed, they’re even thinner on the ground than they were in 2008, when a previous survey asked a similar question, whereas people with technological skills are more plentiful than before.
In order to re-integrate, returnees will need to build their understanding of the China workplace environment and reintegrate, demonstrating local acumen as well as bringing their global acumen to the table. They will need to build their local networks quickly, and “happy hours” don’t quite do the trick. Effective networks are those that are selective and influential and accessed by means of reference from others. Returnees need to get their contacts to introduce them to relevant people. But even before that, they need to understand their needs, wants and strengths, and sharpen their relationship building skills. In short, they will need to develop a personalized strategy to access a changed China. They will need to build out contacts, build up experiences and basic skills, connect with influential professionals and influential leaders, develop self-awareness and learn how to harness their international experience to flourish in a changing China.
